What Is Protein Quantification?
Protein quantification is the process of measuring the concentration of proteins in a given sample. It is a fundamental step in many biological and biochemical workflows, as accurate protein measurement ensures the consistency and reliability of downstream applications such as Western blotting, enzyme assays, immunodetection, and protein purification. Quantification allows researchers to normalize sample inputs, compare expression levels, or assess protein yields across experiments. Various methods are used depending on the sample type and required sensitivity, including absorbance at 280 nm, colorimetric assays like the BCA (Bicinchoninic Acid) assay and Bradford assay, and fluorescent dye-based techniques. Choosing the right method ensures precise, reproducible data that supports meaningful scientific conclusions.
What Is the BCA Protein Assay?
The BCA Protein Assay is a colorimetric technique used to determine total protein concentration in a sample. It is based on the reduction of Cu²⁺ to Cu⁺ by proteins in an alkaline environment (biuret reaction), followed by the formation of a purple-colored complex between Cu⁺ and bicinchoninic acid. This complex absorbs light at 562 nm, and the intensity of the color is directly proportional to the protein amount.
Advantages of the BCA Assay
High Sensitivity: Detects low microgram levels of protein.
Broad Linear Range: Suitable for diverse sample concentrations.
Detergent Compatibility: Tolerates many common buffer components.
Stable Color Development: Color remains stable for over 2 hours, allowing flexibility in measurement time.
Easy Protocol: Ideal for both microplate and test tube formats.
| Feature | BCA Assay | Bradford Assay | Lowry Assay |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | High | Moderate | High |
| Detergent Tolerance | Excellent | Poor | Moderate |
| Linear Range | Broad | Narrow | Moderate |
| Color Stability | >2 hours | <1 hour | Variable |
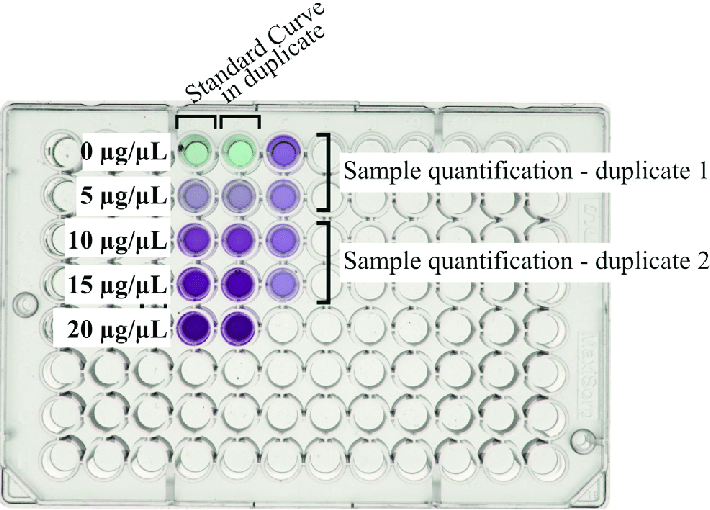
How to Perform the BCA Assay
-
Prepare a standard curve using known concentrations of a standard protein (typically BSA).
-
Mix your samples and standards with the BCA working reagent.
-
Incubate at 37°C for 30 minutes (or room temp for 2 hours).
-
Measure absorbance at 562 nm.
-
Calculate protein concentration from the standard curve.
Tips: Ensure uniform incubation time, avoid interfering substances, and use matched cuvettes or microplate wells for accurate readings.
Applications in Research
The BCA Protein Assay is widely adopted across academic, industrial, and clinical research settings due to its precision and versatility. In academic laboratories, it is routinely used to quantify proteins from cell lysates, tissue homogenates, and purified samples. Researchers rely on its accuracy to normalize protein concentrations for downstream applications such as Western blotting, ELISA, and enzyme activity assays. Its broad compatibility with detergents and common buffer systems makes it ideal for diverse experimental conditions.
In industrial and clinical environments, the BCA assay is instrumental in protein-based product development, including monoclonal antibodies, enzymes, and vaccines. Biopharmaceutical companies use it during formulation development, production monitoring, and quality control. In clinical research, it enables protein quantification in complex biological fluids like plasma, serum, or cerebrospinal fluid, supporting proteomic studies and biomarker analysis. Its ability to integrate seamlessly into both low- and high-throughput workflows makes it a preferred choice in modern life science laboratories.
For researchers seeking dependable protein quantification, choosing a BCA assay that delivers consistent, accurate results can make all the difference. Exploring reliable assay kits ensures smooth progress from sample preparation to analysis, helping laboratories maintain high standards and efficiency. Expert guidance and tailored solutions are often just a message away, ready to support your scientific journey